链表
203.移除链表元素
题意:删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。
示例 1: 输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6 输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
示例 2: 输入:head = [], val = 1 输出:[]
示例 3: 输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7 输出:[]
解答:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
//用原来的链表操作:
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
while(head != null && head.val == val){
head = head.next;
}
ListNode node = head;
while(node != null && node.next != null){
if(node.next.val == val){
node.next = node.next.next;
} else{
node = node.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
//设置一个虚拟头结点:
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode();
dummy.next = head; //虚拟头结点
ListNode node = dummy;
while(node.next != null){
if(node.next.val == val){
node.next = node.next.next;
} else{
node = node.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
707.设计链表
题意:
在链表类中实现这些功能:
- get(index):获取链表中第 index 个节点的值。如果索引无效,则返回-1。
- addAtHead(val):在链表的第一个元素之前添加一个值为 val 的节点。插入后,新节点将成为链表的第一个节点。
- addAtTail(val):将值为 val 的节点追加到链表的最后一个元素。
- addAtIndex(index,val):在链表中的第 index 个节点之前添加值为 val 的节点。如果 index 等于链表的长度,则该节点将附加到链表的末尾。如果 index 大于链表长度,则不会插入节点。如果 index 小于 0,则在头部插入节点。
- deleteAtIndex(index):如果索引 index 有效,则删除链表中的第 index 个节点。
示例:
输入
["MyLinkedList", "addAtHead", "addAtTail", "addAtIndex", "get", "deleteAtIndex", "get"]
[[], [1], [3], [1, 2], [1], [1], [1]]
输出
[null, null, null, null, 2, null, 3]
解释
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
myLinkedList.addAtHead(1);
myLinkedList.addAtTail(3);
myLinkedList.addAtIndex(1, 2); // 链表变为 1->2->3
myLinkedList.get(1); // 返回 2
myLinkedList.deleteAtIndex(1); // 现在,链表变为 1->3
myLinkedList.get(1); // 返回 3
提示:
0 <= index, val <= 1000- 请不要使用内置的 LinkedList 库。
- 调用
get、addAtHead、addAtTail、addAtIndex和deleteAtIndex的次数不超过2000。
解答:
//单链表
class ListNode{
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(){}
ListNode(int val){
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val,ListNode next){
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
class MyLinkedList {
int size;
ListNode head;
public MyLinkedList() {
size = 0;
head = new ListNode(0);
}
public int get(int index) {
if(index < 0 || index > size-1){
return -1;
}
ListNode cur = head;
while(index > 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur.val;
}
public void addAtHead(int val) {
if(size == 0){
head.val = val;
size++;
return;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(val);
dummy.next =head;
head = dummy;
size++;
}
public void addAtTail(int val) {
if(size == 0){
addAtHead(val);
return;
}
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur.next != null){
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = new ListNode(val);
size++;
}
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next =head;
ListNode cur = dummy;
if(index == size){
addAtTail(val);
} else if(index > size){
} else{
while(index > 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
ListNode temp = new ListNode(val);
temp.next = cur.next;
cur.next = temp;
size++;
}
head = dummy.next;
}
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if(index < 0 || index > size-1){
return;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode cur = dummy;
while(index > 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
cur.next = cur.next.next;
head = dummy.next;
size--;
}
}
//双链表
class ListNode{
int val;
ListNode next,prev;
ListNode(){}
ListNode(int val){
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val,ListNode prev,ListNode next){
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
class MyLinkedList {
int size;
ListNode head,tail;
public MyLinkedList() {
size = 0;
head = new ListNode(0);
tail = new ListNode(0);
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
public int get(int index) {
if(index < 0 || index > size-1){
return -1;
}
ListNode cur = this.head;
if(index < size/2){
for(int i = 0;i <= index;i++){
cur = cur.next;
}
}else{
cur = this.tail;
for(int i = size;i > index;i--){
cur = cur.prev;
}
}
return cur.val;
}
public void addAtHead(int val) {
addAtIndex(0,val);
}
public void addAtTail(int val) {
addAtIndex(size,val);
}
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if(index < 0 || index > size){
return;
}
ListNode cur = this.head;
for(int i = 0;i < index;i++){
cur = cur.next;
}
ListNode temp = new ListNode(val);
cur.next.prev = temp;
temp.prev = cur;
temp.next = cur.next;
cur.next = temp;
size++;
}
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if(index < 0 || index > size-1){
return;
}
ListNode cur = this.head;
for(int i = 0;i < index;i++){
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next.next.prev = cur;
cur.next = cur.next.next;
size--;
}
}
206.反转链表
题意:反转一个单链表。
示例: 输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL 输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
解答:
//双指针
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode first = head;
ListNode second = null;
ListNode pre = null;
while(first != null){
second = first.next;
first.next = pre;
pre = first;
first = second;
}
return pre;
}
}
//递归
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
return reverse(null,head);
}
public ListNode reverse(ListNode pre,ListNode first){
if(first == null){
return pre;
}
ListNode second = first.next;
first.next = pre;
return reverse(first,second);
}
}
// 从后向前递归
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode last = reverseList(head.next);//翻转第二个节点之后的节点
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return last;
}
}
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回�交换后的链表。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
解答:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode cur = head;
head = cur.next;
ListNode temp = null;
ListNode pre = null;
while(cur != null && cur.next != null){
if(pre != null){
pre.next = cur.next;//步骤一,可以使用虚拟头节点,就可以避免判断
}
temp = cur.next.next;
cur.next.next = cur;//步骤二
cur.next = temp;//步骤三,交换步骤二和三可以不用加temp节点
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return head;
}
}
//递归
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode cur = head;
head = cur.next;
ListNode last = swapPairs(cur.next.next);
cur.next.next = cur;
cur.next = last;
return head;
}
}
19.删除链表的倒数第 N 个节点
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
进阶:你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
解答:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode cur = dummy;
ListNode temp = cur;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
temp = temp.next;
}
while(temp.next != null){
cur = cur.next;
temp = temp.next;
}
cur.next = cur.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
}
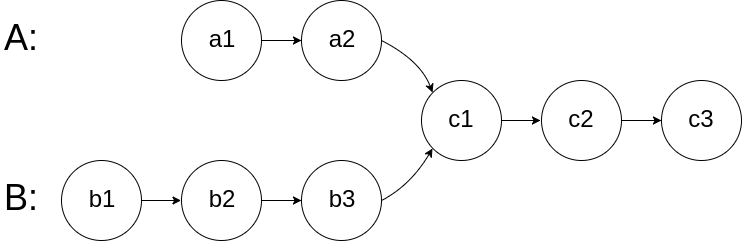
面试题 02.07. 链表相交
同:160.链表相交
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null 。
解答:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode A = headA;
ListNode B = headB;
int cur = 1;
int size = 0;
ListNode temp = null;
while(A != null){
size++;
A = A.next;
}
while(cur <= size && B != null){
A = headA;
B = headB;
for(int i = 0;i < size - cur;i++){
A = A.next;
}
while(B != null){
if(B == A){
cur++;
temp = A;
break;
}
B = B.next;
}
}
return temp;
}
}//另一种方法是同步移动
//合并链表实现同步移动
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode A = headA;
ListNode B = headB;
while(A != B){
if(A == null){
A = headB;
} else{
A = A.next;
}
if(B == null){
B = headA;
} else{
B = B.next;
}
}
return A;
}
}
142.环形链表 II
题意: 给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
为了表示给定链表中的环,使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
说明:不允许修改给定的链表。
解答:
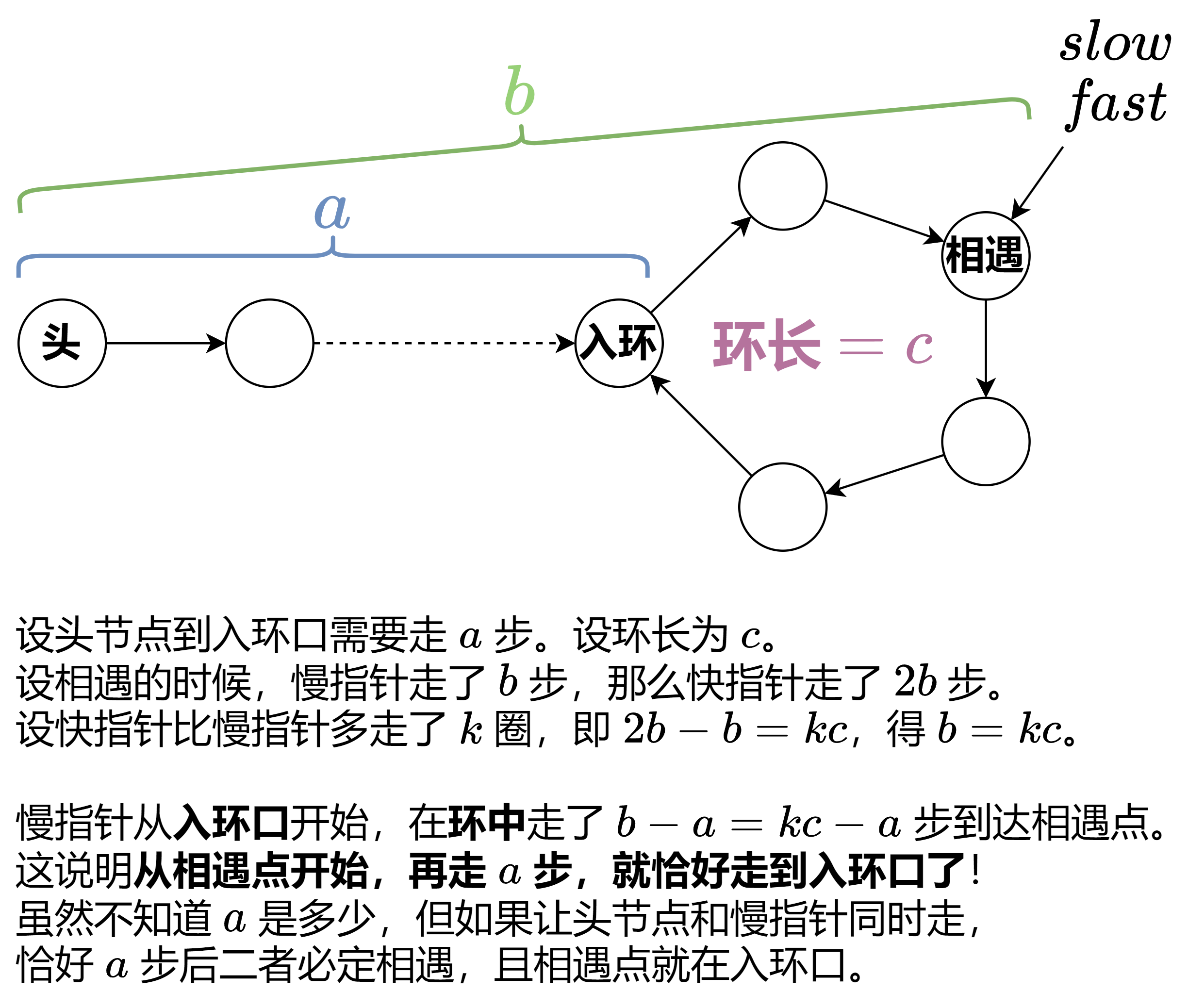
注 1:因为 ,从 开始,再走 a 步,就可以走满 k 圈。想象你在操场上跑步,从入环口开始跑,跑满 k 圈,你现在人在哪?刚好在入环口。
注 2:慢指针从相遇点开始,移动 a 步后恰好走到入环口,但在这个过程中,可能会多次经过入环口。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
boolean iscircle = false;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null && slow.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
iscircle =true;
break;
}
}
if(iscircle == false) return null;
ListNode temp = fast;
fast = fast.next;
slow =head;
while(temp != slow){
while(temp != fast){
if(fast ==slow){
return slow;
} else{
fast = fast.next;
}
}
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
//秒解
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
slow = head;
while(slow != fast){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return null;
}
}
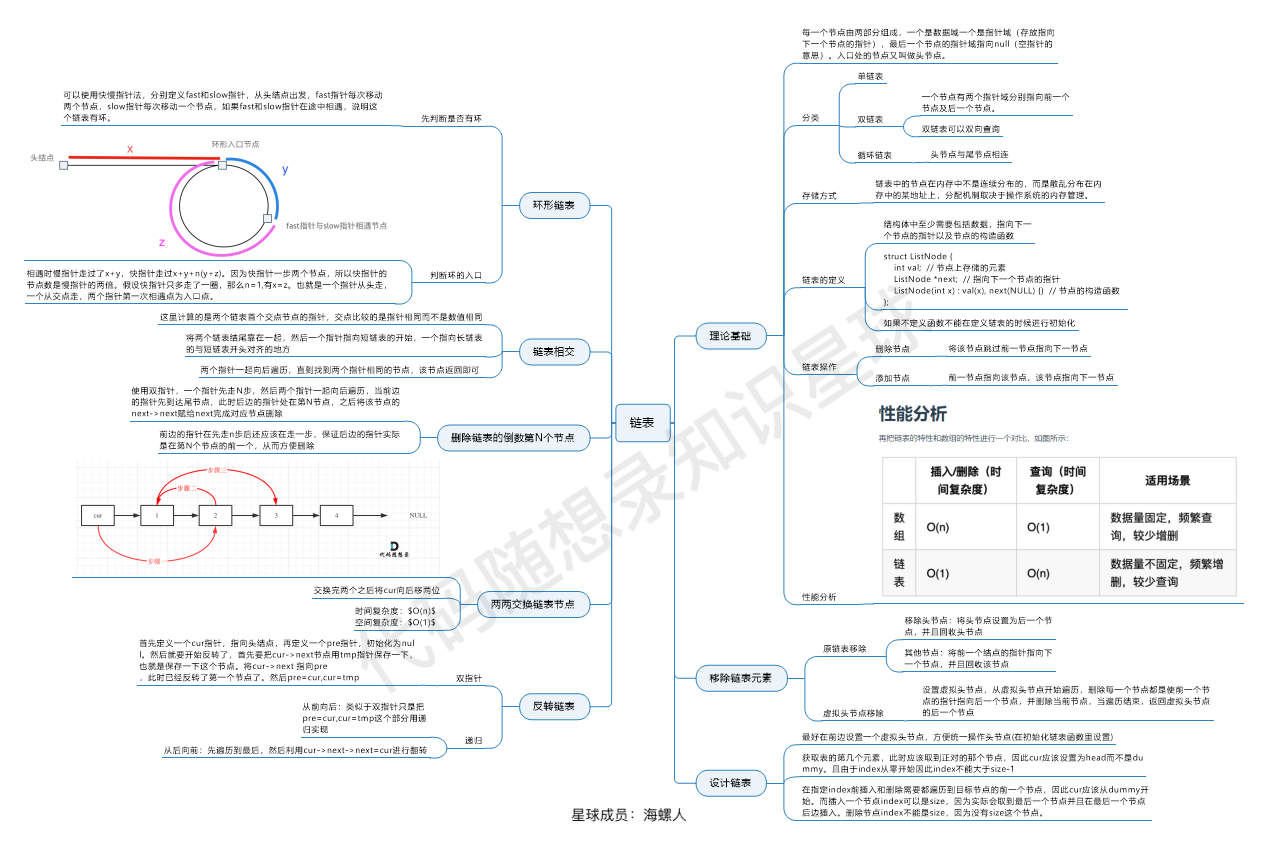
总结
其他
234. 回文链表
给你一个单链表的头节点 head ,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
解答:
// 使用deque
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return false;
else if(head.next == null) return true;
Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<>();
while(head!= null){
deque.addFirst(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
while(deque.size() > 1){
if(deque.pollFirst() != deque.pollLast()) return false;
}
return true;
}
}
//双指针
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return false;
else if(head.next == null) return true;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
ListNode cur1 = head;
ListNode cur2 = reverseList(slow);
while(cur1 != null && cur2 != null){
if(cur1.val != cur2.val) return false;
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return true;
}
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode last = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return last;
}
}
143. 重排链表
给定一个单链表 L 的头节点 head ,单链表 L 表示为:
L0 → L1 → … → Ln - 1 → Ln
请将其重新排列后变为:
L0 → Ln → L1 → Ln - 1 → L2 → Ln - 2 → …
不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
解答:
// 双向链表
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return;
ListNode cur = head.next;
Deque<ListNode> deque = new LinkedList<>();
while(cur != null){
deque.offerLast(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head;
while(deque.size() > 1){
cur.next = deque.pollLast();
cur.next.next = deque.pollFirst();
cur = cur.next.next;
}
if(deque.size() == 1){
cur.next = deque.pollFirst();
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = null;
}
}
// 利用旋转链表
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return;
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while(fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
ListNode second = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
second = reverseList(second);
ListNode first = head;
while(second != null){
ListNode temp = first.next;
first.next = second;
second = second.next;
first.next.next = temp;
first = temp;
}
}
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode last = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return last;
}
}
141. 环形链表
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
解答:
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return false;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast!= null && fast.next!= null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if(slow == fast) return true;
}
return false;
}
}
160. 相交链表
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表��相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交**:**
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
解答:
一种是哈希
一种是循环跳,直到相遇
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> Optional[ListNode]:
p = headA
q = headB
while p != q:
p = p.next if p else headB
q = q.next if q else headA
return p
2. 两数相加
给你两个 非空 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
解答:
# 递归 原地操作
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode], carry=0) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if l1 is None and l2 is None:
return ListNode(carry) if carry else None
if l1 is None:
l1, l2 = l2, l1
carry += l1.val + (l2.val if l2 else 0)
l1.val = carry%10
l1.next = self.addTwoNumbers(l1.next, l2.next if l2 else None, carry//10)
return l1
25. K 个一组翻转链表
给你链表的头节点 head ,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回修改后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
解答:
加入哨兵p0
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseKGroup(self, head: Optional[ListNode], k: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
n = 0
cur = head
while cur:
cur = cur.next
n += 1
dummy = ListNode(next=head) # dummy是虚拟头节点,首次操作时将它当作上一个链表的尾节点,所以首次操作后成为正确链表的虚拟头节点
p0 = dummy # p0位置的节点是上上一个的链表的尾,且它指向下一个未操作的链表的头
pre = None
cur = head
while n >= k:
n -= k
for _ in range(k):
nxt = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = nxt
nxt = p0.next
nxt.next = cur
p0.next = pre
p0 = nxt
return dummy.next
138. 随机链表的复制
给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝。 深拷贝应该正好由 n 个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random 指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点 。
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
val:一个表示Node.val的整数。random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从0到n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为null。
你的代码 只 接受原链表的头节点 head 作为传入参数。
解答:
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, x: int, next: 'Node' = None, random: 'Node' = None):
self.val = int(x)
self.next = next
self.random = random
"""
class Solution:
def copyRandomList(self, head: 'Optional[Node]') -> 'Optional[Node]':
if head is None:
return None
p0 = head
while p0: #拷贝val和next
p0.next = Node(x=p0.val, next=p0.next)
p0 = p0.next.next
dummy = head.next
p0 = head
while p0: #拷贝random
p0.next.random = p0.random.next if p0.random else None
p0 = p0.next.next
p0 = head
while p0:
p1 = p0.next
p0.next = p0.next.next
p1.next = p1.next.next if p1.next else None
p0 = p0.next
return dummy
148. 排序链表
给你链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
解答:
方法一归并排序
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def midNode(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
slow = fast = head
pre = head
while fast:
fast = fast.next.next if fast.next else None
pre = slow
slow = slow.next
pre.next = None
return slow
def MergeTwoLists(self, list1: Optional[ListNode], list2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
p0 = dummy = ListNode(0)
first, second = list1, list2
while first and second:
if first.val <= second.val:
p0.next = first
first = first.next
else:
p0.next = second
second = second.next
p0 = p0.next
p0.next = first if first else second
return dummy.next
def sortList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if head is None or head.next is None:
return head
list2 = self.sortList(self.midNode(head))
list1 = self.sortList(head)
return self.MergeTwoLists(list1, list2)
方法一的归并是自顶向下计算,需要 O(logn) 的递归栈开销。
方法二将其改成自底向上计算,空间复杂度优化成 O(1)。
自底向上的意思是:
- 首先,归并长度为 1 的子链表。例如 [4,2,1,3],把第一个节点和第二个节点归并,第三个节点和第四个节点归并,得到 [2,4,1,3]。
- 然后,归并长度为 2 的子链表。例如 [2,4,1,3],把前两个节点和后两个节点归并,得到 [1,2,3,4]。
- 然后,归并长度为 4 的子链表。
- 依此类推,直到归并的长度大于等于链表长度为止,此时链表已经是有序的了。
具体算法:
- 遍历链表,获取链表长度 length。
- 初始化步长 step=1。
- 循环直到 step≥length。
- 每轮循环,从链表头节点开始。
- 分割出两段长为 step 的链表,合并,把合并后的链表插到新链表的末尾。重复该��步骤,直到链表遍历完毕。
- 把 step 扩大一倍。回到第 4 步。
23. 合并 K 个升序链表
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
解答:
方法一:分治
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def MergeTwoLists(self, list1: Optional[ListNode], list2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
p0 = dummy = ListNode(0)
first, second = list1, list2
while first and second:
if first.val <= second.val:
p0.next = first
first = first.next
else:
p0.next = second
second = second.next
p0 = p0.next
p0.next = first if first else second
return dummy.next
def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[Optional[ListNode]]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
k = len(lists)
if k == 1:
return lists[0]
elif k == 0:
return None
left = self.mergeKLists(lists[0:k//2])
right = self.mergeKLists(lists[k//2:])
return self.MergeTwoLists(left, right)
方法二:最小堆
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
ListNode.__lt__ = lambda a, b :a.val < b.val
class Solution:
def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[Optional[ListNode]]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
cur = dummy = ListNode()
h = [head for head in lists if head]
heapify(h) # 堆化,类似 java 的优先对列
while h:
node = heappop(h)
if node.next:
heappush(h, node.next)
cur.next = node
cur = cur.next
return dummy.next
146. LRU 缓存
请你设计并实现一个满足 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存 约束的数据结构。
实现 LRUCache 类:
LRUCache(int capacity)以 正整数 作为容量capacity初始化 LRU 缓存int get(int key)如果关键字key存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回-1。void put(int key, int value)如果关键字key已经存在��,则变更其数据值value;如果不存在,则向缓存中插入该组key-value。如果插入操作导致关键字数量超过capacity,则应该 逐出 最久未使用的关键字。
函数 get 和 put 必须以 O(1) 的平均时间复杂度运行。
解答:
// 采用双向循环链表
class LRUCache {
private static class Node{
int key, value;
Node pre, next;
Node(int k, int v){
key = k;
value = v;
}
}
private final int capacity;
private final Node dummy = new Node(0, 0); // 头节点
private final Map<Integer, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
dummy.next = dummy;
dummy.pre = dummy;
}
public int get(int key) {
Node node = getNode(key);
return node == null ? -1 : node.value;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
Node node = getNode(key);
if(node != null){
node.value = value;
return;
}
node = new Node(key, value);
map.put(key, node);
pushFront(node);
if(map.size() > capacity){
Node backNode = dummy.pre;
map.remove(backNode.key);
remove(backNode);
}
}
private Node getNode(int key){
if(!map.containsKey(key)){
return null;
}
Node node = map.get(key);
remove(node);
pushFront(node);
return node;
}
private void remove(Node x) {
x.pre.next = x.next;
x.next.pre = x.pre;
}
private void pushFront(Node x){
x.pre = dummy;
x.next = dummy.next;
x.next.pre = x;
x.pre.next = x;
}
}
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj.get(key);
* obj.put(key,value);
*/