贪心算法
题目分类
理论基础
贪�心的本质是选择每一阶段的局部最优,从而达到全局最优。
贪心的套路
唯一的难点就是如何通过局部最优,推出整体最优。
最好用的策略就是举反例,如果想不到反例,那么就试一试贪心。
有时候通过(accept)了贪心的题目,但都不知道自己用了贪心算法,**因为贪心有时候就是常识性的推导,所以会认为本应该就这么做!
题目:链表:环找到了,那入口呢?,这种题目确实需要数学简单推导。
贪心一般解题步骤:想清楚局部最优是什么,如何推导出全局最优。
455.分发饼干
假设你是一位很棒的家长,想要给你的孩子们一些小饼干。但是,每个孩子最多只能给一块饼干。
对每个孩子 i,都有一个胃口值 g[i],这是能让孩子们满足胃口的饼干的最小尺寸;并且每块饼干 j,都有一个尺寸 s[j] 。如果 s[j] >= g[i],我们可以将这个饼干 j 分配给孩子 i ,这个孩子会得到满足。你的目标是尽可能满足越多数量的孩子,并输出这个最大数值。
解答:
class Solution {
public int findContentChildren(int[] g, int[] s) {
int cnt = 0;
Arrays.sort(g);
Arrays.sort(s);
int j = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < s.length; i++){
if(j < g.length && s[i] >= g[j]){
cnt++;
j++;
}
}
return cnt;
}
}
376. 摆动序列
如果连续数字之间的差严格地在正数和负数之间交替,则数字序列称为摆动序列。第一个差(如果存在的话)可能是正数或负数。少于两个元素的序列也是摆动序列。
解答:
class Solution {
public int wiggleMaxLength(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) return 0;
if(nums.length == 1) return nums.length;
int cnt = 0;
int i = 1;
while(i < nums.length && nums[i] == nums[i -1]) i++;
if(i == nums.length) return 1;
boolean flag = (nums[i-1] > nums[i]);
for(; i < nums.length; i++){
if(nums[i-1] == nums[i]) continue;
if(flag == (nums[i-1] > nums[i])){
flag = !flag;
cnt++;
}
}
return ++cnt;
}
}
//DP
class Solution {
public int wiggleMaxLength(int[] nums) {
// 0 i 作为波峰的最大长度
// 1 i 作为波谷的最大长度
int dp[][] = new int[nums.length][2];//记录摆动序列的最大长度
dp[0][0] = dp[0][1] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
dp[i][0] = dp[i][1] = 1;
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++){
if(nums[j] > nums[i]){
dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i][1], dp[j][0] + 1);
}
if(nums[j] < nums[i]){
dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i][0], dp[j][1] + 1);
}
}
}
return Math.max(dp[nums.length-1][0], dp[nums.length-1][1]);
}
}
//j
class Solution {
public int wiggleMaxLength(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length <= 1) return nums.length; //如果数组长度为0或1��,则返回数组长度
int up = 1, down = 1; //记录上升和下降摆动序列的最大长度
for(int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++){
if(nums[i] > nums[i-1]) up = down + 1;
else if(nums[i] < nums[i-1]) down = up + 1;
}
return Math.max(up, down); //返回上升和下降摆动序列的最大长度
}
}
53. 最大子序和
给定一个整数数组 nums ,找到一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
解答:
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length == 0) return 0;
int maxSum = nums[0];
int curSum = nums[0];
for(int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++){
curSum = Math.max(nums[i], curSum + nums[i]);
maxSum = Math.max(curSum, maxSum);
}
return maxSum;
}
}
122.买卖股票的最佳时机 II
给定一个数组,它的第 i 个元素是一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。你可以尽可能地完成更多的交易(多次买卖一支股票)。
注意:你不能同时参与多笔交易(你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票)。
解答:
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int[] dp = new int[prices.length];//存放第i天时的最大收益
dp[0] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++){
dp[i] = dp[i-1] + Math.max(0, prices[i]-prices[i-1]);
}
return dp[prices.length-1];
}
}
55. 跳跃游戏
给定一个非负整数数组,你最初位于数组的第一个位置。
数组中的每个元素代表你在该位置可以跳跃的最大长度。
判断你是否能够到达最后一个位置。
解答:
//DP
class Solution {
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
int len = nums.length;
boolean[] dp = new boolean[len];
dp[0] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < len-1; i++){
int j = 1;
while(dp[i] && j+i < len && j <= nums[i]){
dp[j+i] = true;
if(j++ +i == len-1) return true;
}
}
return dp[len-1];
}
}
class Solution {
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length == 1) return true;
int coverage = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <= coverage; i++){//判断的条件很关键
coverage = Math.max(coverage, nums[i] + i);
if(coverage >= nums.length-1) return true;
}
return false;
}
}
45.跳跃游戏 II
给定一个非负整数数组,你最初位于数组的第一个位置。
数组中的每个元素代表你在该位置可以跳跃的最大长度。
你的目标是使用最少的跳跃次数到达数组的最后一个位置。
解答:
class Solution {
public int jump(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0 || nums.length == 1) return 0;
int maxcoverage = nums[0], curcoverage = 0;
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
maxcoverage = Math.max(maxcoverage, nums[i] + i);
if(maxcoverage >= nums.length-1) return ++cnt;//达到条件就跳出
if(curcoverage == i){//超过覆盖范围就跳转,其他情况是还在范围内可以不跳转
curcoverage = maxcoverage;
cnt++;
}
}
return 0;
}
}
1005.K 次取反后最大化的数组和
给定一个整数数组 A,我们只能用以下方法修改该数组:我们选择某个索引 i 并将 A[i] 替换为 -A[i],然后总共重复这个过程 K 次。(我们可以多次选择同一个索引 i。)
以这种方式修改数组后,返回数组可能的最大和。
解答:
//常规做法
class Solution {
public int largestSumAfterKNegations(int[] nums, int k) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) return 0;
int negative_cnt = 0;//负数
int sum = 0;
Arrays.sort(nums);
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if(nums[i] < 0){
negative_cnt++;
if(negative_cnt <= k) nums[i] = -nums[i];
}
if(i == negative_cnt){//此时i为第一个正数的索引
if(negative_cnt < k){
if(i > 0){
if(nums[i] > nums[i-1]){
sum -= nums[i-1];
sum += (((k-negative_cnt) & 1) == 0) ? nums[i-1] : -nums[i-1];
} else {
nums[i] = (((k-negative_cnt) & 1) == 0) ? nums[i] : -nums[i];
}
} else {//全为正数
nums[0] = (((k-negative_cnt) & 1) == 0) ? nums[0] : -nums[0];
}
}
}
sum += nums[i];
}
if(negative_cnt == nums.length && k > negative_cnt) sum = (((k-negative_cnt) & 1) == 0) ? sum : sum-2*nums[nums.length-1];//全为负数
return sum;
}
}
//贪心算法
class Solution {
public int largestSumAfterKNegations(int[] nums, int k) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) return 0;
int sum = 0;
nums = IntStream.of(nums)
.boxed()
.sorted((a, b) -> Math.abs(b) - Math.abs(a))
.mapToInt(Integer::intValue)
.toArray();//按照绝对值排序
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if(nums[i] < 0 && k > 0){
k--;
nums[i] = -nums[i];
}
if(i == nums.length-1){//消化剩余的k
nums[i] = ((k & 1) == 0) ? nums[i] : -nums[i];
}
sum += nums[i];
}
return sum;
}
}
class Solution {
public int largestSumAfterKNegations(int[] nums, int k) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) return 0;
int negative_cnt = 0;//负数
int sum = 0;
Arrays.sort(nums);
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if(nums[i] < 0 && k > 0){
k--;
nums[i] = -nums[i];
}
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
if(k > 0){//消化剩余的k
nums[0] = ((k & 1) == 0) ? nums[0] : -nums[0];
}
sum = Arrays.stream(nums).sum();//
return sum;
}
}
Absolute value sorting:
IntStream.of(nums): Creates an IntStream from the input arraynums.boxed(): Converts the IntStream of primitiveintvalues into a Streamof wrapped Integer objects. This is necessary because the next operation (sorting) needs to work with objects, not primitives. .sorted((o1, o2) -> Math.abs(o2) - Math.abs(o1)):- Sorts the stream using a custom comparator
Math.abs()takes the absolute value of each number- The comparison
o2 - o1(rather thano1 - o2) creates a descending order - So numbers are sorted by their absolute values in descending order
- For example: [-5, 2, -3, 1] would be sorted as [-5, -3, 2, 1]
.mapToInt(Integer::intValue): Converts the Streamback to an IntStream by extracting the primitive int value from each Integer object .toArray(): Finally converts the IntStream into a regular int array
134. 加油站
在一条环路上有 N 个加油站,其中第 i 个加油站有汽油 gas[i] 升。
你有一辆油箱容量无限的的汽车,从第 i 个加油站开往第 i+1 个加油站需要消耗汽油 cost[i] 升。你从其中的一个加油站出发,开始时油箱为空。
如果你可以绕环路行驶一周,则返回出发时加油站的编号,否则返回 -1。
说明:
- 如果题目有解,该答案即为唯一答案。
- 输入数组均为非空数组,且长度相同。
- 输入数组中的元素均为非负数。
解答:
class Solution {
public int canCompleteCircuit(int[] gas, int[] cost) {
int past = 0, cur = 0;
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < gas.length; i++){
cur += gas[i] - cost[i];
if(cur < 0){
past += cur;//记录负的
cur = 0;
res = i+1;//从正的开始
}
}
if(past + cur < 0) return -1;
else return res;
}
}
135. 分发糖果
老师想给孩子们分发糖果,有 N 个孩子站成了一条直线,老师会根据每个孩子的表现,预先给他们评分。
你需要按照以下要求,帮助老师给这些孩子分发糖果:
- 每个孩子至少分配到 1 个糖果。
- 相邻的孩子中,评分高的孩子必须获得更多的糖果。
那么这样下来,老师至少需要准备多少颗糖果呢?
解答:
class Solution {
public int candy(int[] ratings) {
int len = ratings.length;
if(len < 1) return len;
int result = 0;
int[] dp = new int[len];
dp[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < len; i++){//Left
dp[i] = (ratings[i] > ratings[i-1]) ? dp[i-1]+1 : 1;
}
for(int i = len-2; i >= 0; i--){/
dp[i] = (ratings[i] > ratings[i+1]) ? Math.max(dp[i+1]+1, dp[i]) : dp[i];
}
result = Arrays.stream(dp).sum();
return result;
}
}
406.根据身高重建队列
假设有打乱顺序的一群人站成一个队列,数组 people 表示队列中一些人的属性(不一定按顺序)。每个 people[i] = [hi, ki] 表示第 i 个人的身高为 hi ,前面 正好 有 ki 个身高大于或等于 hi 的人。
请你重新构造并返回输入数组 people 所表示的队列。返回的队列应该格式化为数组 queue ,其中 queue[j] = [hj, kj] 是队列中第 j 个人的属性(queue[0] 是排在队列前面的人)。
解答:
class Solution {
public int[][] reconstructQueue(int[][] people) {
LinkedList<int[]> que = new LinkedList<>();
Arrays.sort(people, (a, b) -> {//lambda表达式,内部类
if(a[0] == b[0]) return a[1] - b[1];
return b[0] - a[0];
});
for(int[] arr : people){
que.add(arr[1], arr);//Linkedlist.add(index, value),会将value插入到指定index里。
}
return que.toArray(new int[people.length][2]);
}
}
452. 用最少数量的箭引爆气球
在二维空间中有许多球形的气球。对于每个气球,提供的输入是水平方向上,气球直径的开始和结束坐标。由于它是水平的,所以纵坐标并不重要,因此只要知道开始和结束的横�坐标就足够了。开始坐标总是小于结束坐标。
一支弓箭可以沿着 x 轴从不同点完全垂直地射出。在坐标 x 处射出一支箭,若有一个气球的直径的开始和结束坐标为 xstart,xend, 且满足 xstart ≤ x ≤ xend,则该气球会被引爆。可以射出的弓箭的数量没有限制。 弓箭一旦被射出之后,可以无限地前进。我们想找到使得所有气球全部被引爆,所需的弓箭的最小数量。
给你一个数组 points ,其中 points [i] = [xstart,xend] ,返回引爆所有气球所必须射出的最小弓箭数。
解答:
class Solution {
public int findMinArrowShots(int[][] points) {
Arrays.sort(points, (a, b) -> {
if(a[0] == b[0]) return Integer.compare(a[1], b[1]);
return Integer.compare(a[0], b[0]);
});
int res = points.length;
int temp = points[0][1];
for(int i = 1; i < points.length; i++){
if(points[i][0] <= temp){
res--;
temp = Math.min(temp, points[i][1]);
}
else temp = points[i][1];
}
return res;
}
}
435. 无重叠区间
给定一个区间的集合,找到需要移除区间的最小数量,使剩余区间互不重叠。
注意: 可以认为区间的终点总是大于它的起点。 区间 [1,2] 和 [2,3] 的边界相互“接触”,但没有相互重叠。
解答:
class Solution {
public int eraseOverlapIntervals(int[][] intervals) {
Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> {
if(a[0] == b[0]) return Integer.compare(a[1], b[1]);
return Integer.compare(a[0], b[0]);
});
int res = 0;
int temp = intervals[0][1];
for(int i = 1; i < intervals.length; i++){
if(intervals[i][0] < temp){
res++;
if(intervals[i][1] < temp) temp = intervals[i][1];
}
else temp = intervals[i][1];
}
return res;
}
}
763.划分字母区间
字符串 S 由小写字母组成。我们要把这个字符串划分为尽可能多的片段,同一字母最多出现在一个片段中。返回一个表示每个字符串片段的长度的列表。
解答:
class Solution {
public List<Integer> partitionLabels(String s) {
int[] arr = new int[128];
char[] ss = s.toCharArray();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < ss.length; i++){
arr[ss[i] - 'a'] = i;//字母出现的最后w
}
int maxindex = 0;
int last = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < ss.length; i++){
maxindex = Math.max(arr[ss[i]-'a'], maxindex);
if(maxindex == ss.length-1){
list.add(ss.length-1 - last);
break;
}
if(i == maxindex){
list.add(maxindex - last);
last = i;
}
}
return list;
}
}
56. 合并区间
给出一个区间的集合,请合并所有重叠的区间。
解答:
class Solution {
public int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) {
if(intervals.length == 0 || intervals.length == 1) return intervals;
Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> {
if(a[0] == b[0]) return Integer.compare(a[1], b[1]);
return Integer.compare(a[0], b[0]);
});
LinkedList<int[]> res = new LinkedList<>();
int temp = intervals[0][1];
int pre = intervals[0][0];
for(int i = 1; i < intervals.length; i++){
if(intervals[i][0] > temp){
res.add(new int[]{pre, temp});
pre = intervals[i][0];
temp = intervals[i][1];
}
else temp = Math.max(intervals[i][1], temp);
if(i == intervals.length - 1){
res.add(new int[]{pre, temp});
}
}
return res.toArray(new int[res.size()][2]);
}
}
738.单调递增的数字
给定一个非负整数 N,找出小于或等于 N 的最大的整数,同��时这个整数需要满足其各个位数上的数字是单调递增。
(当且仅当每个相邻位数上的数字 x 和 y 满足 x <= y 时,我们称这个整数是单调递增的。)
解答:
// int[]
class Solution {
public int monotoneIncreasingDigits(int n) {
if(n < 10) return n;
List<Integer> num = new ArrayList<>();
while(n > 0){
num.addFirst(n%10);
n /= 10;
}
int[] res = new int[num.size()];
res[0] = num.get(0);
int start = 0;
Boolean flag = false;
for(int i = 1; i < num.size(); i++){
if(res[i-1] > num.get(i)){
flag = true;
break;
}else{
res[i] = num.get(i);
}
start = res[i-1] == num.get(i) ? start : i;
}
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < res.length; i++){
if(flag){
if(i <= start) sum = 10*sum + res[i];
else sum *= 10;
if(i == res.length-1) sum--;
} else {
sum = 10*sum + res[i];
}
}
return sum;
}
}
// char[]
class Solution {
public int monotoneIncreasingDigits(int n) {
if(n < 10) return n;
String s = String.valueOf(n);
char[] ss = s.toCharArray();
int start = ss.length;
for(int i = ss.length-2; i >= 0; i--){
if(ss[i] > ss[i+1]){
start = i+1;
ss[i]--;
}
}
for(int i = start; i < ss.length; i++){
ss[i] = '9';
}
return Integer.valueOf(String.valueOf(ss));
}
}
968.监控二叉树
给定一个二叉树,我们在树的节点上安装摄像头。
节点上的每个摄影头都可以监视其父对象、自身及其直接子对象。
计算监控树的所有节点所需的最小摄像头数量。
解答:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int res = 0;
public int minCameraCover(TreeNode root) {
// 对根节点的状态做检验,防止根节点是无覆盖状态.
if(CameraCover(root) == 0){
res++;
}
return res;
}
/**
节点的状态值:
0 表示无覆盖
1 表示 有摄像头
2 表示有覆盖
后序遍历,根据左右节点的情况,来判读 自己的状态
*/
public int CameraCover(TreeNode node) {//后序遍历
if(node == null) return 2;
int left = CameraCover(node.left);
int right = CameraCover(node.right);
if(left == 2 && right == 2){// 如果左右节点都覆盖了的话, 那么本节点的状态就应该是无覆盖,没有摄像头
return 0;
} else if(left == 0 || right == 0){// 左右节点都是无覆盖状态,那 根节点此时应该放一个摄像头
res++;
return 1;
} else{// 左右节点的 状态为 (1,1) (1,2) (2,1) 也就是左右节点至少存在 1个摄像头,
return 2;
}
}
}
总结
贪心专题汇聚为一张图:
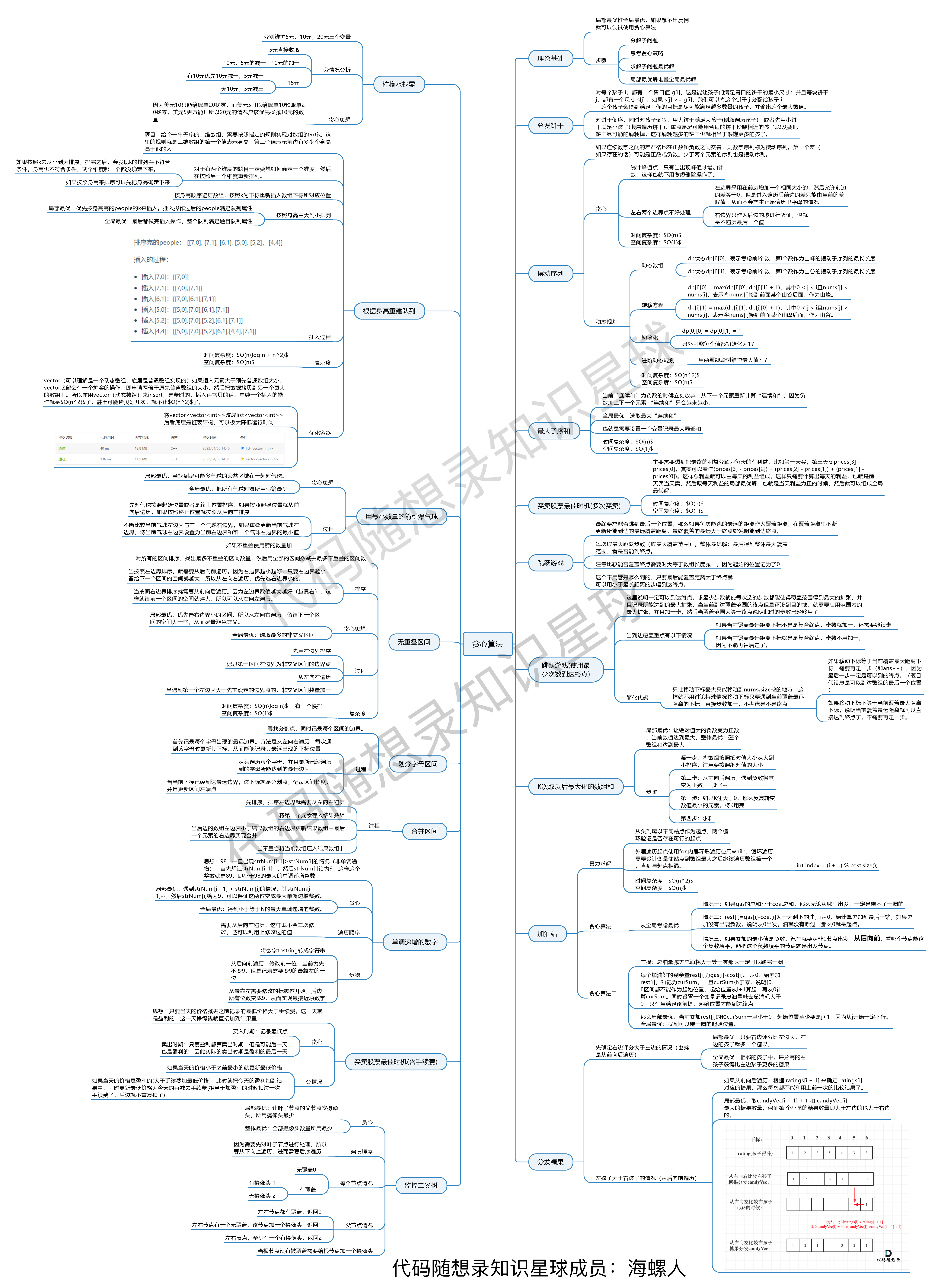
其他
649. Dota2 参议院
Dota2 的世界里有两个阵营:Radiant(天辉)和 Dire(夜魇)
Dota2 参议院由来自两派的参议员组成。现在参议院希望对一个 Dota2 游戏里的改变作出决定。他们以�一个基于轮为过程的投票进行。在每一轮中,每一位参议员都可以行使两项权利中的一项:
- 禁止一名参议员的权利:参议员可以让另一位参议员在这一轮和随后的几轮中丧失所有的权利。
- 宣布胜利:如果参议员发现有权利投票的参议员都是同一个阵营的,他可以宣布胜利并决定在游戏中的有关变化。
给定一个字符串代表每个参议员的阵营。字母 “R” 和 “D” 分别代表了 Radiant(天辉)和 Dire(夜魇)。然后,如果有 n 个参议员,给定字符串的大小将是 n。
以轮为基础的过程从给定顺序的第一个参议员开始到最后一个参议员结束。这一过程将持续到投票结束。所有失去权利的参议员将在过程中被跳过。
假设每一位参议员都足够聪明,会为自己的政党做出最好的策略,你需要预测哪一方最终会宣布胜利并在 Dota2 游戏中决定改变。输出应该是 Radiant 或 Dire。
解答:
// 利用队列
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.LinkedList;
class Solution {
public String predictPartyVictory(String senate) {
Deque<Character> deque = new LinkedList<>();
for(char c : senate.toCharArray()) deque.addLast(c);
int r = 0, d = 0;
while(deque.size() > 1){
int len = deque.size();
int sum = len;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
char c = deque.pollFirst();
if (c == 'R') {
if(d > 0){
d--;
} else {
r++;
deque.addLast(c);
}
} else {
if(r > 0) {
r--;
} else {
d++;
deque.addLast(c);
}
}
}
if(sum == deque.size()) break;
}
return deque.isEmpty() ? null : (deque.pollFirst() == 'R' ? "Radiant" : "Dire");
}
}
// b
class Solution {
public String predictPartyVictory(String senate) {
byte[] senators = senate.getBytes();
boolean r = true, d = true;
int flag = 0;
while(r && d){
r = false;
d = false;
for(int i = 0; i < senate.length(); i++){
if(senators[i] == 'R'){
if(flag < 0){
senators[i] = 0;
}
else r = true;
flag++;
}
if(senators[i] == 'D'){
if(flag > 0){
senators[i] = 0;
}
else d = true;
flag--;
}
}
}
return r ? "Radiant" : "Dire";
}
}